anterior acetabular labral tear test|hip impingement labral tear : retailer The McCarthy Test is a clinical test used in the diagnosis of a hip labral tear. The shearing force-producing painful popping, clicking, or catching while performing the test indicates a possible hip labrum tear. [1] Clinically Relevant Anatomy. .
For underwater applications, a KMS plastic bearing features a Flow-Thru Technology™ design that allows suspended particles to enter the bearing and flow through without clogging and .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Class B autoclaves enable the sterilization of both wrapped and unwrapped instruments, no matter their type and complexity. The fractionated vacuum reduces the air in the sterilization chamber through repeated evacuation and .
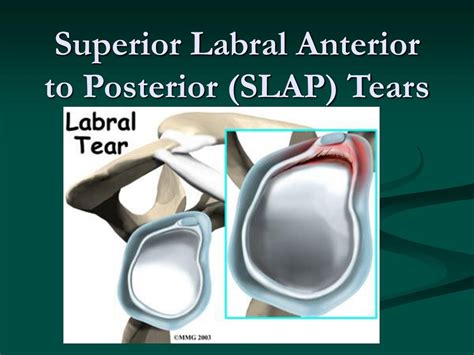
An acetabular labral tear can cause pain if the labrum is torn, frayed, or damaged. Labral tears cause groin pain or pain in the anterior side of the hip, and less commonly buttock pain. This mechanically induced pathology is thought to result from excessive forces at the hip joint. For example, a tear could . See more
The acetabular labrum is a fibro-cartilaginous rim, which encompasses the circumference of the acetabulum. It helps to keep the head of the femurinside the acetabulum, . See moreIn studies of patients with a labral tear, researchers have attributed the injury to a variety of causes: 1. Direct trauma - e.g. motor accidents, falling with or without a hip dislocation, . See more
The differential diagnosis of labral tears may include the following diagnoses: 1. Athletic pubalgia 2. Snapping_Hip 3. Septic (Infectious) Arthritis 4. Piriformis syndrome 5. Contusion 6. Strain 7. Osteitis pubis 8. Trochanteric Bursitis 9. Avascular necrosis of the femoral head 10. Fracture 11. Dislocation 12. Inguinalor femoral hernia 13. Legg-C. See more
The FADIR (flexion, adduction, internal rotation) test is used for the examination of femoroacetabular impingement syndrome, anterior labral tear and iliopsoas tendinitis. The .The McCarthy Test is a clinical test used in the diagnosis of a hip labral tear. The shearing force-producing painful popping, clicking, or catching while performing the test indicates a possible hip labrum tear. [1] Clinically Relevant Anatomy. .An acetabular labral tear can cause pain if the labrum is torn, frayed, or damaged. Labral tears cause groin pain or pain in the anterior side of the hip, and less commonly buttock pain. [1] This mechanically induced pathology is thought to result from excessive forces at the hip joint .The FADIR (flexion, adduction, internal rotation) test is used for the examination of femoroacetabular impingement syndrome, anterior labral tear and iliopsoas tendinitis. The premise of this test is that flexion and adduction motions approximates the .
The McCarthy Test is a clinical test used in the diagnosis of a hip labral tear. The shearing force-producing painful popping, clicking, or catching while performing the test indicates a possible hip labrum tear. [1] Clinically Relevant Anatomy. Hip Joint Anatomy [2]The most consistent physical exam finding in patients with acetabular labral tears is a positive anterior hip-impingement test [13, 35, 92]. This is performed with the patient supine with the hip and knee at 90° of flexion.
Labral tears in the hip are now becoming widely recognised as a source of anterior hip/groin pain and intra-articular pathology. The prevalence of acetabular labral tears in some populations presenting with hip or groin pain has been reported to be between 22% and 55% (Narvani et al., 2003; McCarthy et al., 2001).
small anterior superior labral tear
right anterior acetabular labral tear
how to measure final specific gravity with a refractometer
Imaging scans. A hip labral tear rarely occurs by itself. In most cases, other structures within the hip joint also have injuries. X-rays are excellent at visualizing bone. They can check for arthritis and for structural problems.Diagnosing acetabular labral tears with hip traction sonography: a case series. Journal of Ultrasound 24:4, 547-553. [Crossref] Yuwei Liu, Wei Lu, Kan Ouyang, Zhenhan Deng. 2021. The imaging evaluation of acetabular labral lesions. Journal of . Patients with labral tear complain about anterior hip or groin pain most commonly with a most consistent physical examination called positive anterior hip impingement test. Magnetic resonance arthrography is a reliable radiographic examination with arthroscopy being the gold standard.
This paper aims to assess the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and latest evidence-based treatment of acetabular labral tears. The acetabular labrum contributes to the stability of the hip. Labral tears may lead to significant pain and disability, although many are asymptomatic. A hip labral tear is a traumatic tear of the acetabular labrum, mostly common seen in acetabular dysplasia, that may lead to symptoms of internal snapping hip as well hip locking with hip range of motion. Diagnosis generally requires an MR arthrogram of the hip joint in question.An acetabular labral tear can cause pain if the labrum is torn, frayed, or damaged. Labral tears cause groin pain or pain in the anterior side of the hip, and less commonly buttock pain. [1] This mechanically induced pathology is thought to result from excessive forces at the hip joint .
The FADIR (flexion, adduction, internal rotation) test is used for the examination of femoroacetabular impingement syndrome, anterior labral tear and iliopsoas tendinitis. The premise of this test is that flexion and adduction motions approximates the .The McCarthy Test is a clinical test used in the diagnosis of a hip labral tear. The shearing force-producing painful popping, clicking, or catching while performing the test indicates a possible hip labrum tear. [1] Clinically Relevant Anatomy. Hip Joint Anatomy [2]
The most consistent physical exam finding in patients with acetabular labral tears is a positive anterior hip-impingement test [13, 35, 92]. This is performed with the patient supine with the hip and knee at 90° of flexion.
Labral tears in the hip are now becoming widely recognised as a source of anterior hip/groin pain and intra-articular pathology. The prevalence of acetabular labral tears in some populations presenting with hip or groin pain has been reported to be between 22% and 55% (Narvani et al., 2003; McCarthy et al., 2001). Imaging scans. A hip labral tear rarely occurs by itself. In most cases, other structures within the hip joint also have injuries. X-rays are excellent at visualizing bone. They can check for arthritis and for structural problems.Diagnosing acetabular labral tears with hip traction sonography: a case series. Journal of Ultrasound 24:4, 547-553. [Crossref] Yuwei Liu, Wei Lu, Kan Ouyang, Zhenhan Deng. 2021. The imaging evaluation of acetabular labral lesions. Journal of .
Patients with labral tear complain about anterior hip or groin pain most commonly with a most consistent physical examination called positive anterior hip impingement test. Magnetic resonance arthrography is a reliable radiographic examination with arthroscopy being the gold standard. This paper aims to assess the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and latest evidence-based treatment of acetabular labral tears. The acetabular labrum contributes to the stability of the hip. Labral tears may lead to significant pain and disability, although many are asymptomatic.
how to measure refractive index using a refractometer
nondisplaced anterosuperior labral tear
This manual provides instructions for installing, operating, maintaining and troubleshooting two models of autoclaves: the Slow Exhaust Autoclave Model 8000-DSE and the Rapid Exhaust Autoclave Model 9000-D. Key details .
anterior acetabular labral tear test|hip impingement labral tear